Introduction to Automobile
Introduction to Automobile – An automobile is a self-propelled vehicle that travels on land. It consists an internal combustion engine which provides the power and the vehicle runs on the wheels. The primary function of an automobile is to carries people and goods from one place to another. All bikes, cars, truck etc. include in it.
History of automobile
In the early day’s people used bullock carriage or other animals such as camel, horse etc. to transport good and human from one place to another. In use of these animals one big problem encounter is that they could not travel for long distance and for long time. So the necessary of a machine is arrive which can have satisfied these function. (Introduction to Automobile)
After a great effort of scientist an automobile come into existence in 1769, when a French engineer Captain Nicholas Cugnot design the first road vehicle propelled by its own power. It is a steam engine automobile but his design proved to be impractical. First steam carriage built by Richard Trevithick in 1801 in England. In the year 1860, first internal combustion engine is developed by J.J.E. Lenoir. He used coal gas as fuel. (Introduction to Automobile)
There is no compression stroke before burring of fuel. In the year 1867, Nikolaus Otto and Eugen Langer used compression stroke in that engine so the power of engine will increase. In the year 1876, Nikolaus Otto developed first four stroke spark ignition engine.
After this several engineers (Dugald Clerk, James Robson and Karl Benz) developed two stroke engine. In the year 1880, Karl Benz in Germany developed a tricycle propelled by an internal combustion engine. In the year 1892, Rudolf Diesel developed first four stroke compression ignition engine. In the year 1920 a stratified charge engine developed which can run on both petrol and diesel.
Ricardo developed a jet ignited stratified charged engine. In the year 1957 Wankel developed a rotary type internal combustion engine.1.1.3.2 How does an automobile work ?
In an automobile many parts work together and make an automobile run. These all parts are known as basic component of an automobile. There are: (Introduction to Automobile)
1. Engine:
Engine is the power unit in automobile. The main function of engine is to convert the chemical energy into mechanical energy by burning of fuel. This mechanical energy uses to rotate the wheels.
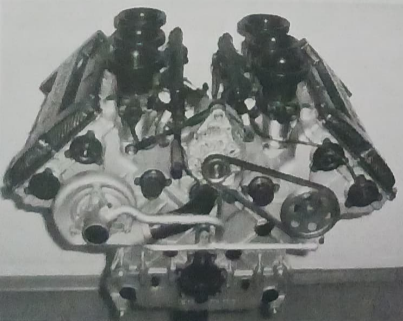
2. Power train:
When the engine produces power some mediators required to carry power from engine to wheels of vehicle. These mediators are known as power train. It includes clutch, gear box, propeller shaft, differential gear, rear axle etc. (Introduction to Automobile)
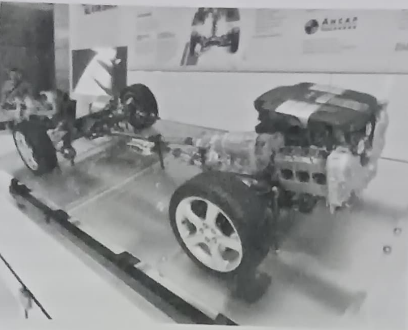
3. Wheels:
Wheel is use to convert the rolling motion of engine into linear motion of vehicle. (Introduction to Automobile)

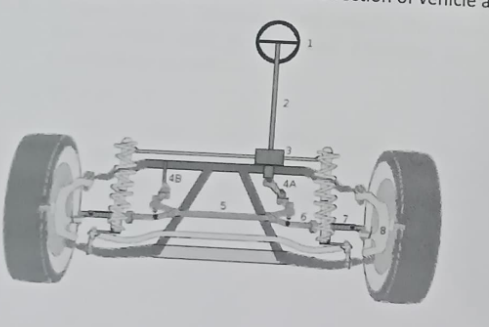
4. Steering system
Steering system is use to control the direction of vehicle according to the driver need. (Introduction to Automobile)
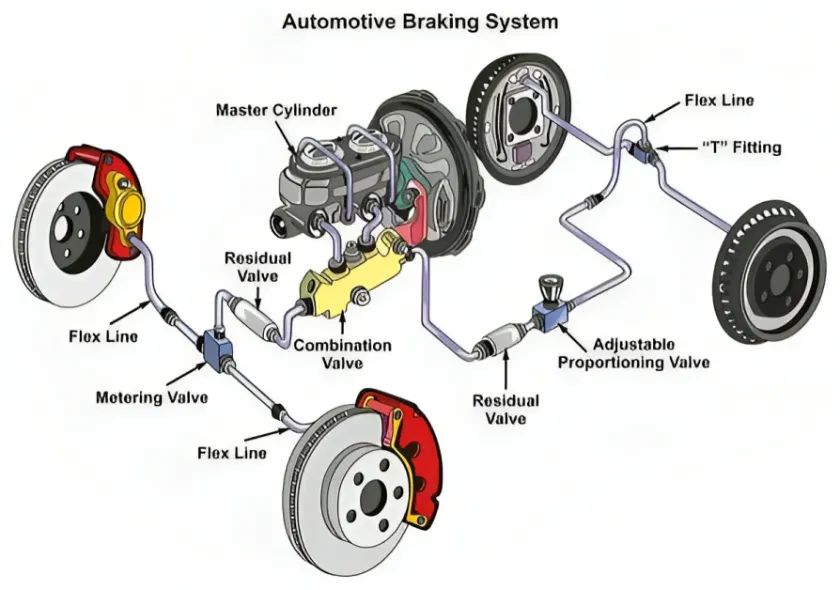
5. Braking system
Braking system is use to control the speed of vehicle. It stops of slow down the vehicle when the driver need. (Introduction to Automobile)
6. Electric system:
Electric system is used in ignition system as well as in head light, brake light, indicator, Air conditioning system, horn etc. (Introduction to Automobile)
7. Body
It covers all components of vehicle and gives it a better appearance and also provides space for driver, passengers and language. (Introduction to Automobile)

Automotive Industry in India
In 2020, India was the fifth-largest auto market, with “3.49 million units combined sold in the passenger and commercial vehicles categories. It was the seventh largest manufacturer of commercial
vehicles in 2019 . (Introduction to Automobile)
The two wheelers segment dominate the market in terms of volume owing to a growing middle class and a young population. Moreover, the growing interest of the companies in exploring the rural markets further aided the growth of the sector .
India is also a prominent auto exporter and has strong export growth expectations for the near future. In addition, several initiatives by the Government of India and major automobile players in the Indian market is expected to make India a leader in the two-wheeler and four-wheeler market in the world by 2020 . (Introduction to Automobile)
Market Size
Domestic automobiles production increased at 2.36% CAGR between FY16-20 with 26.36 million vehicles being manufactured in the country in FY20. Overall, domestic automobiles sales increased at 1.29% CAGR between FY16-FY20 with 21.55 million vehicles being sold in FY20 .
Two wheelers and passenger vehicles dominate the domestic Indian auto market. Passenger car sales are dominated by small and mid-sized cars. Two wheelers and passenger cars accounted for 80.8% and 12.9% market share, respectively, accounting for a combined sale of over 20.1 million vehicles in FY20. Two-wheeler sales stood at 1,195,445 units in March 2021, compared with 1,846,613 units in March 2020, recording a decline of 35.26% . (Introduction to Automobile)
Passenger vehicle (PV) sales stood at 279,745 units in March 2021, compared with 2,17,879 units in March 2020, registering a growth of 28.39%. (Introduction to Automobile)
As per Federation of Automobile Dealers Associations (FADA), PV sales in December 2020 stood at 271,249 units, compared with 218,775 units in December 2019, registering a 23.99% growth.
Overall, automobile export reached 4.77 million vehicles in FY20, growing at a CAGR of 6.94% during FY16-FY20. Two wheelers made up 73.9% of the vehicles exported, followed by passenger vehicles at 14.2%, three wheelers at 10.5% and commercial vehicles at 1.3%. (Introduction to Automobile)
Investment / Major Development
In order to keep up with the growing demand, several auto makers have started investing heavily in various segments of the industry during the last few months. The industry has attracted Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) worth US$ 25.40 billion between April 2000 and December 2020, according to the data released by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) .
Some of the developments in the recent past are :
1. In 2019-20, the total passenger vehicles sales reached “2.8 million, while “2.7 million units were sold in FY21 .
2. In February 2021, the Delhi government started the process to set up 100 vehicle battery charging points across the state to push adoption of electric vehicles .
3. In January 2021, Lamborghini announced it is aiming to achieve sales in India higher than the 2019 levels, after recovering from pandemic-induced disruptions .
4. In January 2021, Tesla, the electric car maker, set up a R&D centre in Bengaluru and registered its subsidiary as Tesla India Motors and Energy Private Limited .
5. In November 2020, Mercedes Benz partnered with the State Bank of India to provide attractive interest rates, while expanding customer base by reaching out to potential HNI customers of the
bank.
Hyundai Motor India invested “Rs. 3,500 crore (US$ 500 million) in FY20, with an eye to gain the market share. This investment is a part of Rs. 7,000 crore (US$ 993 million) commitment made by the company to the Tamil Nadu government in 2019.
In October 2020, Kinetic Green, an electric vehicles manufacturer, announced plan to set up a manufacturing facility for electric golf carts besides a battery swapping unit in Andhra Pradesh. The two projects involving setting up a manufacturing facility for electric golf carts and a battery swapping unit will entail an investment of Rs. 1,750 crore (US$ 236.27 million) .
In October 2020, Japan Bank for International Cooperation (IBIC) agreed to provide US$ 1 billion (Rs. 7,400 crore) to SBI (State Bank of India) for funding the manufacturing and sales business of suppliers and dealers of Japanese automobile manufacturers and providing auto loans for the purchase of Japanese automobiles in India .
In September 2020, Toyota Kirloskar Motors announced investments of more than Rs 2,000 crore (US$ 272.81 million) in India directed towards electric components and technology for domestic
customers and exports.
During early September 2020, Mahindra & Mahindra singed a MoU with Israel-based REE Automotive to collaborate and develop commercial electric vehicles .
In April 2020, TVS Motor Company bought UK’s iconic sporting motorcycle brand, Norton, for a sum of about Rs. 153 crore (US$ 21.89 million), making its entry into the top end (above 850cc) segment of the superbike market .
In March 2020, Lithium Urban Technologies partnered with renewable energy solutions provider, Fourth Partner Energy, to build charging infrastructure across the country .
. In January 2020, Tata AutoComp Systems, the auto-components arm of Tata Group entered a joint venture with Beijing-based Prestolite Electric to enter the electric vehicle (EV) components market .
Road Ahead
The automobile industry is supported by various factors such as availability of skilled labour at low cost, robust R&D centres, and low-cost steel production. The industry also provides great opportunities for investment and direct and indirect employment to skilled and unskilled labour .
Indian automotive industry (including component manufacturing) is expected to reach Rs. 16.16-18.18 trillion (US$ 251.4-282.8 billion) by 2026 .
The Indian auto industry is expected to record strong growth in 2021-22, post recovering from effects of COVID-19 pandemic. Electric vehicles, especially two-wheelers, are likely to witness positive sales in 2021-22 . (Introduction to Automobile)
Also Read :- Introduction To Deisel Engine Mechanic








